Diagnostic Services
Diagnostic Services

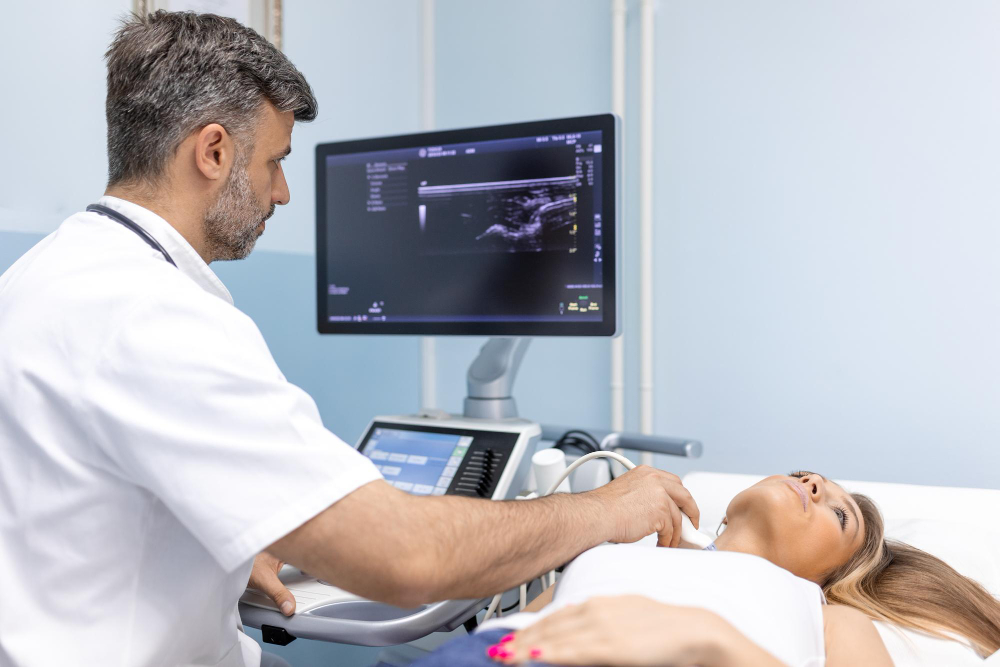
2D Echo
A 2D echocardiogram, or 2D echo, is a non-invasive imaging test that uses ultrasound waves to create detailed images of the heart's structure and function. It provides two-dimensional images of the heart chambers, valves, and blood flow patterns in real time. A transducer placed on the chest emits sound waves, which bounce off the heart and create images on a monitor. 2D echo helps diagnose heart conditions such as valve defects, heart muscle abnormalities, and fluid accumulation around the heart.
Fluoroscopy
Fluoroscopy is a medical imaging technique that uses a continuous X-ray beam to create real-time moving images of the internal structures of a patient's body. It is commonly used to visualize dynamic processes such as swallowing, joint movements, and cardiac catheterization. During fluoroscopy, the X-ray images are displayed on a monitor, allowing healthcare professionals to observe the procedure in progress and make real-time adjustments. This technology provides valuable information for diagnosing and guiding various medical procedures.
Digital X-Ray
Digital X-ray is an advanced imaging technology used to capture detailed images of the body's internal structures. It employs digital sensors to produce high-quality radiographs swiftly and efficiently. Compared to traditional X-rays, it offers clearer images, quicker results, and the ability to easily store and transmit data for analysis and diagnosis. Digital X-ray technology reduces radiation exposure for patients and enables healthcare providers to enhance diagnostic accuracy, leading to more effective treatment planning and improved patient care.
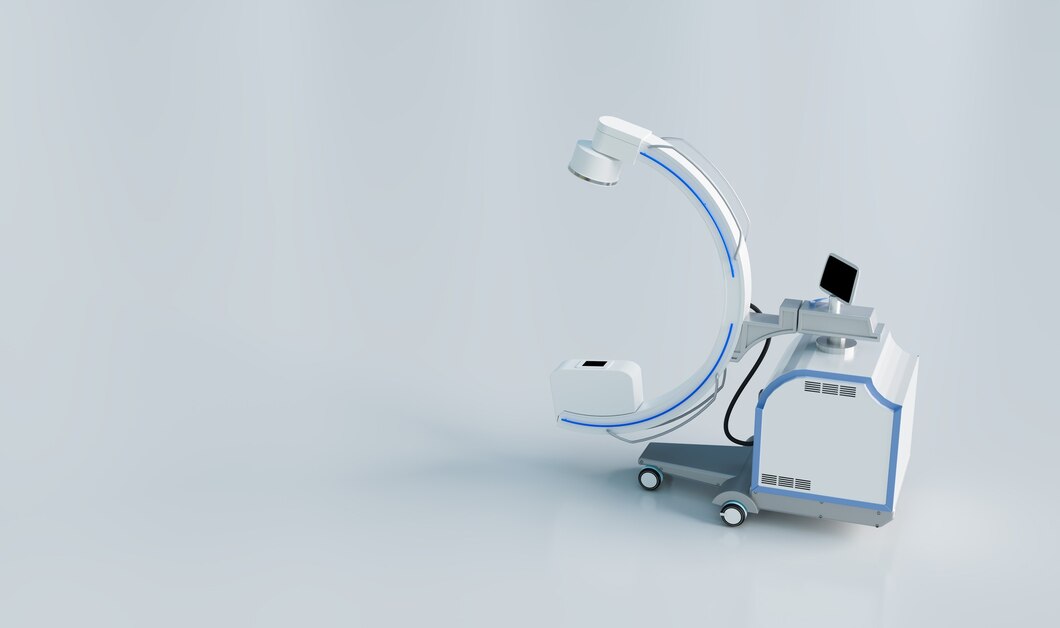
C-Arm
A C-arm is a specialized medical imaging device consisting of a C-shaped arm with an X-ray source and detector that can move around the patient. It provides real-time fluoroscopic imaging, allowing healthcare professionals to visualize internal structures during surgical procedures, such as orthopedic surgeries, cardiac interventions, and vascular procedures. The C-arm's flexibility and versatility make it invaluable for guiding surgical instruments, placing implants, and ensuring accurate positioning, ultimately improving patient outcomes and reducing the need for additional interventions.
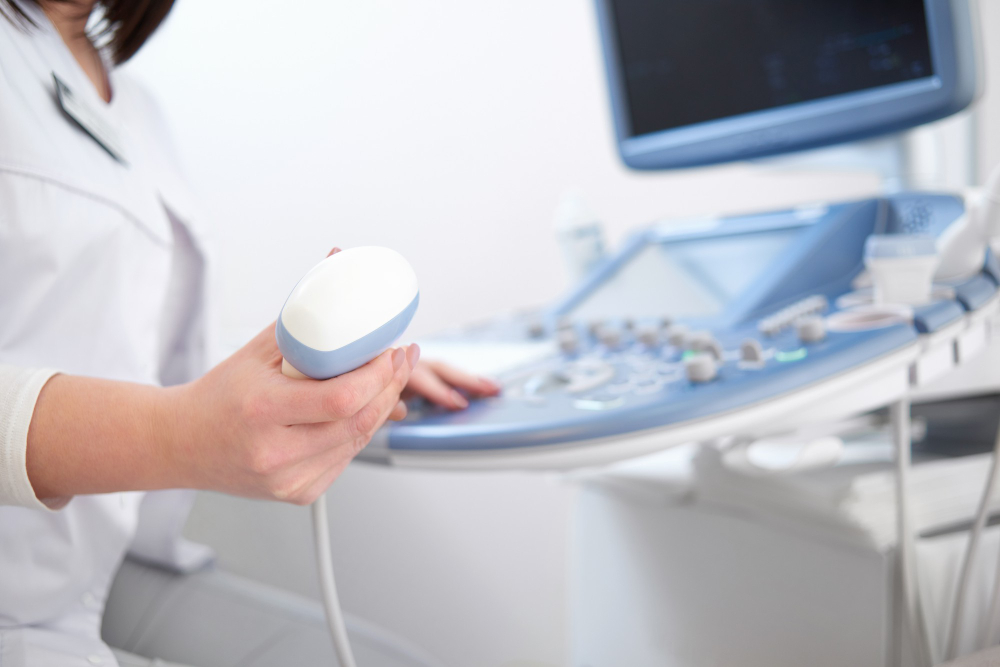
Colour Doppler
Colour Doppler is an imaging technique used in medical diagnostics to assess blood flow and detect abnormalities in blood vessels and organs. It utilizes Doppler ultrasound technology to measure the speed and direction of blood flow, represented by colour-coded images overlaid on traditional ultrasound images. Colour Doppler is commonly used to diagnose conditions such as deep vein thrombosis, arterial stenosis, and heart valve disorders. It provides valuable information for clinicians to evaluate vascular health and plan appropriate treatment strategies.

Digital ECG
Digital ECG (Electrocardiogram) is a modern technique for recording and analyzing the electrical activity of the heart. It involves placing electrodes on the patient's chest, limbs, or torso to capture the heart's electrical signals. Unlike traditional ECG, which records data on paper, digital ECG utilizes electronic sensors to convert the signals into digital data for computer analysis and storage. This technology allows for quick and accurate interpretation of cardiac rhythms, aiding in the diagnosis and management of various heart conditions.
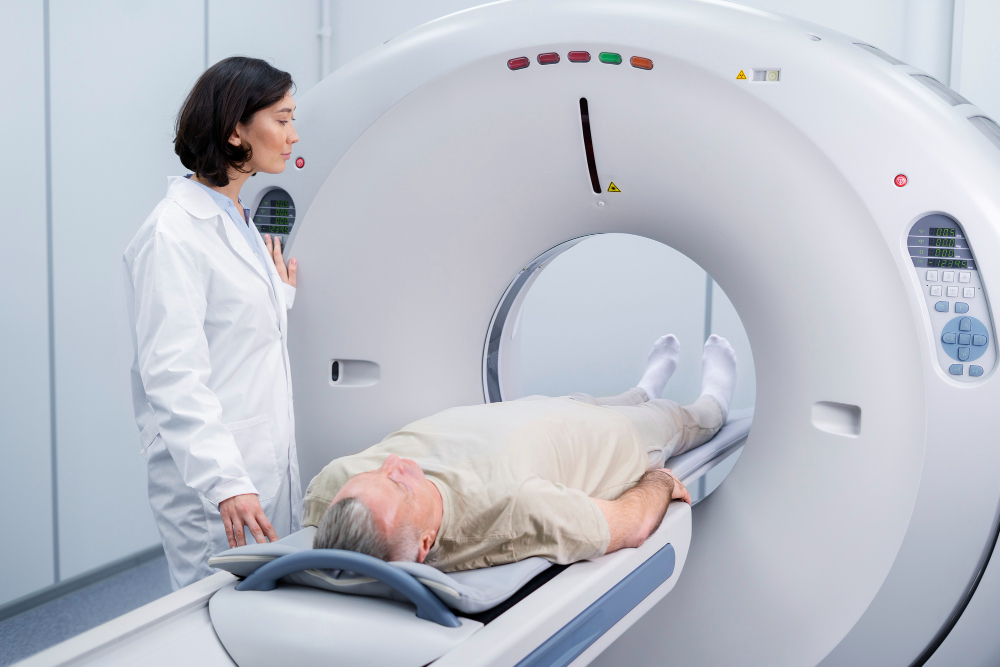
CT Scan
A CT scan, or computed tomography scan, is a non-invasive medical imaging technique that uses X-rays and computer processing to create detailed cross-sectional images of the body. It provides valuable information about internal organs, bones, soft tissues, and blood vessels, aiding in the diagnosis and treatment of various medical conditions such as injuries, tumors, infections, and abnormalities. CT scans are fast, painless, and widely used in healthcare for their ability to reveal precise anatomical structures and abnormalities. However, due to the use of X-rays, precautions are taken to minimize radiation exposure, especially in vulnerable populations such as pregnant women.
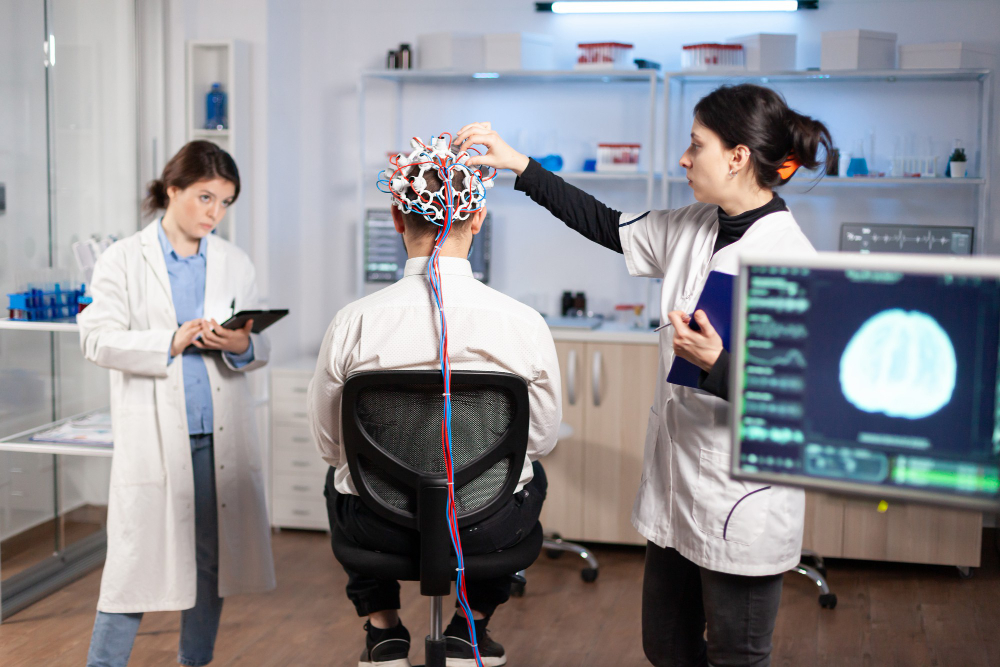
EEG
EEG, or electroencephalography, is a non-invasive neuroimaging technique that measures electrical activity in the brain. It involves placing electrodes on the scalp to record the brain's electrical impulses, which are then amplified and displayed as wave patterns on a monitor. EEG is used to diagnose and monitor various neurological conditions such as epilepsy, brain tumors, sleep disorders, and cognitive impairments. It helps clinicians understand brain function, identify abnormalities in brain waves, assess seizure activity, and evaluate responses to treatments like medication or brain stimulation. EEG is an essential tool in neurology and neuroscience research, providing valuable insights into brain activity and function.
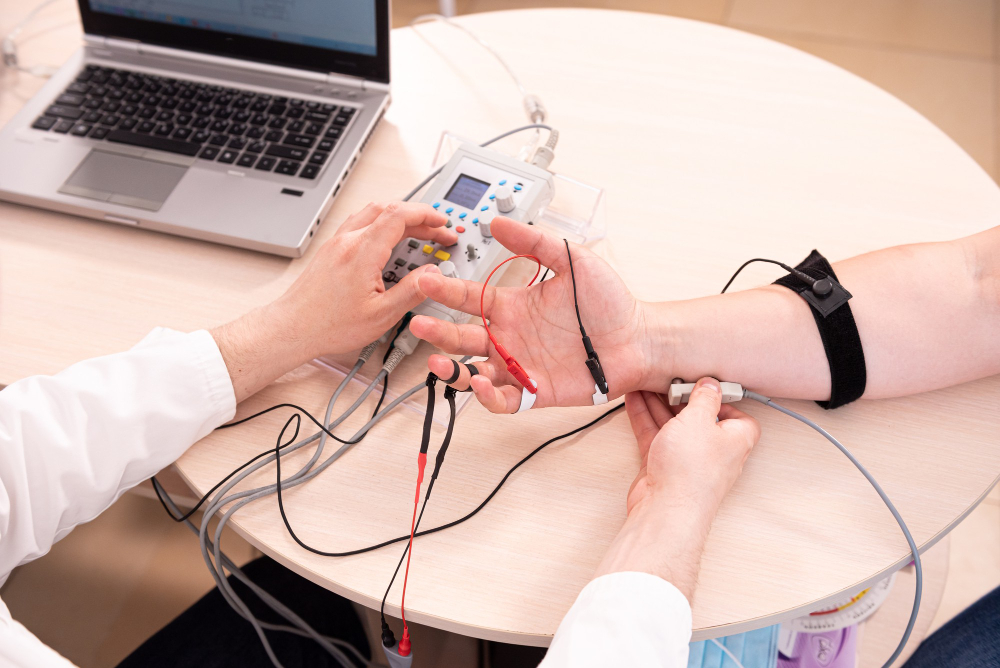
Nerve Conduct Study
A nerve conduction study (NCS) assesses nerve and muscle function by measuring electrical signals' speed and strength along nerve pathways. Electrodes placed on the skin deliver small electrical impulses to stimulate nerves, recording their responses. NCS aids in diagnosing conditions like carpal tunnel syndrome, peripheral neuropathy, and nerve injuries by revealing nerve damage, conduction blockages, and muscle disorders. Typically combined with electromyography (EMG), NCS offers a comprehensive evaluation of nerve and muscle health, guiding treatment plans and monitoring progress in neurological disorders.


